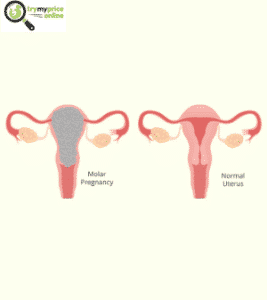
Molar pregnancy, When an egg and sperm combine wrong during fertilization, a noncancerous tumor instead of a healthy placenta emerges. The pregnancy terminates when the tumor, or mole, is unable to nourish a developing embryo. A hydatidiform mole is another name for it.
Related: Protein creatinine ratio pregnancy calculator and its usage

all the diffrent types of pregnancy test
Molar pregnancy
Molar pregnancies are extremely uncommon, yet they can happen to anyone.
If you do any of the following, you’re more likely to have a molar pregnancy:
Are you under the age of 20?
Are you over 40 years old?
Have you ever had a molar pregnancy?
Have had at least two miscarriages
Live in various parts of the world, such as the Philippines, Southeast Asia, and Mexico.
Women of European ancestry in the United States have a higher chance of molar pregnancy than women of other ethnicities.
You can download a molar pregnancy guide from amazon
Related: Pregnancy test calculator week by week
What sorts of molar pregnancies are there?
Complete and partial pregnancies are the two types of molar pregnancies.
The placental tissue is defective in full molar pregnancies, and no embryo develops.
The pregnancy hormone HCG, which is produced by normal placentas during normal pregnancies, is still formed and produced by the tumor.
Many pregnancy tests check for HCG levels.
When an aberrant placenta grows alongside an embryo, this is known as a partial molar pregnancy.
Embryos in these situations had significant birth abnormalities.
The embryo is swiftly overtaken by the growing tumor.
Related: B6 And Unisom during Pregnancy: Is It Safe?
What causes pregnancy in the molars?
When specific genetic mistakes occur during the fertilization of an egg by a sperm, molar pregnancies develop.
A placenta forms in a healthy pregnancy to nourish the developing embryo.
Instead of a placenta, a tumor grows inside the uterus in a molar pregnancy.
A molar pregnancy almost never involves a growing embryo.
When cells remain in the uterus after a miscarriage, a normal pregnancy, or an ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancies can occur.
A fertilized egg implants outside the uterus in an ectopic pregnancy.
Related: Cvs pregnancy test positive faint line and its meaning
clear blue pregnancy test results faint line
What does it look like?
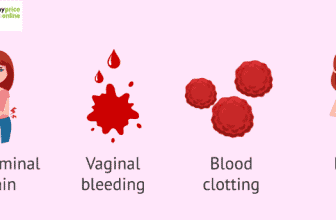
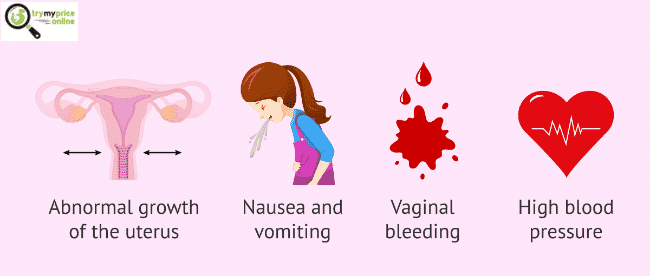
The following are the most prevalent signs and symptoms of it.
During the first three months of pregnancy, you may have vaginal bleeding.
Nausea and vomiting are severe.
Preeclampsia is a syndrome that affects expecting mothers.
High amounts of HCG
Abdominal growth that occurs significantly more quickly than in a successful pregnancy
There is no fetal movement or heartbeat.
Grape-like cysts protruding from the vaginal canal.
Related: Pregnancy test with salt
What is the treatment for it?
The majority of molar pregnancies end naturally.
Grape-like cysts pass naturally out of the womb and through the vaginal canal in these circumstances.
Molar pregnancies in some women require therapy.
Dilation and curettage (the removal of tissue using a tool) are combined with a vacuum to remove all aberrant tissue from the uterus.
A hysterectomy, or tumor resection of the entire uterus, is required to manage it in rare situations.
Related: Unisom for pregnancy nausea and how to use it

All in all, It is impossible to avoid a molar pregnancy. If you’ve had a recent molar pregnancy, you can lower your risk of difficulties by waiting one year after your first molar pregnancy to have another.
References: