Cholestasis of pregnancy is a liver issue. The usual flow of bile from the gallbladder is slowed or stopped. Itching and discoloration of the skin, eyes, and mucous result from this (jaundice). Cholestasis of pregnancy can develop early in pregnancy. However, it occurs more frequently in the second and third trimesters. It usually disappears after a few days of delivery. High bile levels can pose major issues for your unborn child.
Related: Pregnancy announcement creative ideas

a faint positive pregnancy test
Cholestasis of pregnancy
The etiology of pregnant cholestasis is unknown to medical professionals. They are aware that this occurs:
Bile is produced by your liver. During digestion, bile aids in the breakdown of lipids.
Bile is stored in the gallbladder.
The hormones released by your body during pregnancy alter the function of your gallbladder. Bile may slow or cease flowing as a result of this.
Bile accumulates in the liver and then leaks into the bloodstream.
You can download a guide about cholestasis of pregnancy from amazon
Related: Protein creatinine ratio pregnancy calculator and its usage
What are the signs and symptoms of pregnant cholestasis?
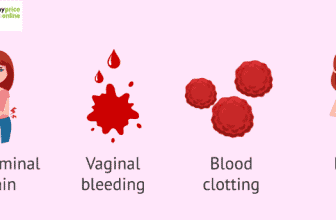
Severe itching is the most common symptom of pregnant Cholestasis of pregnancy.
Pruritus is another term for it. It could appear on any part of the body.
However, it is more common on the palms and soles of the feet. It could be even worse at night. Other signs and symptoms include:
Although not common, pain in the stomach (abdomen) can occur.
The stool is a light hue (bowel movements)
Although not frequent, jaundice is a yellow coloration of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
Cholestasis symptoms can mimic those of other medical diseases. Always get medical advice from your doctor.
Related: Cvs pregnancy test positive faint line and its meaning
How is pregnant cholestasis diagnosed?
If you have significant itching, your doctor is likely to suspect you have pregnant cholestasis.
Lab tests will assist in the confirmation of the diagnosis. These tests may be performed on you:
Tests on the liver include bile acid levels in the blood. In pregnant cholestasis, this test result is high.
Prothrombin time is one of the other lab tests. This test determines the effectiveness of your blood clotting.
Other diagnostics, such as an ultrasound examination of the bile tubes, may be performed.
Related: Pregnancy test with salt

different types of pregnancy test
How is pregnant cholestasis treated?
You and your doctor will talk about the optimal treatment for you based on the following factors:
Your childbirth
Your current health and medical history
How sick are you?
How effectively you respond to specific medications, surgeries, or therapies
The goals of treating pregnant cholestasis are to alleviate itching and avoid problems. Treatment options could include:
Medicine. To help relieve itching and reduce bile production.
Serum total bile acid is measured. Bile levels in your blood can be measured. This assists your healthcare professional in determining treatment options.
Fetal surveillance. Your healthcare professional may examine your unborn child for any concerns.
Early arrival. Between 37 and 38 weeks of pregnancy, you may have your baby.
This will reduce the danger to your child. This could be accomplished by a vaginal delivery aided by medication to induce labor.
You could also have a cesarean section.
Depending on your symptoms, test results, and pregnancy history, your healthcare professional may recommend that you deliver even sooner.
Related: Pregnancy test calculator week by week
Cholestasis of pregnancy

In the end, remember that cholestasis of pregnancy is a condition in which the gallbladder’s normal bile flow is slowed or stopped.
References: